Banking codes like routing numbers and ABA transit numbers may seem like a confusing jumble of digits. However, understanding their differences is crucial for ensuring smooth and secure financial transactions. This comprehensive guide will unravel the mystery, clarifying what these codes are, how they differ, and why they matter.
Introduction
In today’s digital age, financial transactions happen at lightning speed, often with just a few clicks or taps. Behind the scenes, though, a complex system of codes and identifiers facilitates the accurate routing of funds between accounts and institutions.
Two key players in this process are routing numbers and ABA transit numbers. While they may sound similar, there are distinct differences in their purposes and uses.
Unveiling the Mystery: Routing Numbers vs ABA Transit Numbers Explained
A routing number, also known as an ABA routing transit number or RTN, is a nine-digit code that identifies the financial institution involved in a domestic transaction within the United States. It acts as a unique address, enabling the secure and efficient transfer of funds between banks.
On the other hand, an ABA transit number is a specific type of routing number used by the Federal Reserve Banks for processing Fedwire fund transfers and participating in other funds transfer services. It serves as a identifier for financial institutions involved in these specialized transactions.
While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there is a subtle yet important distinction: routing numbers encompass both domestic transactions and international wire transfers, while ABA transit numbers are primarily used for domestic and Fedwire transactions within the United States.
What are ABA Transit Numbers?
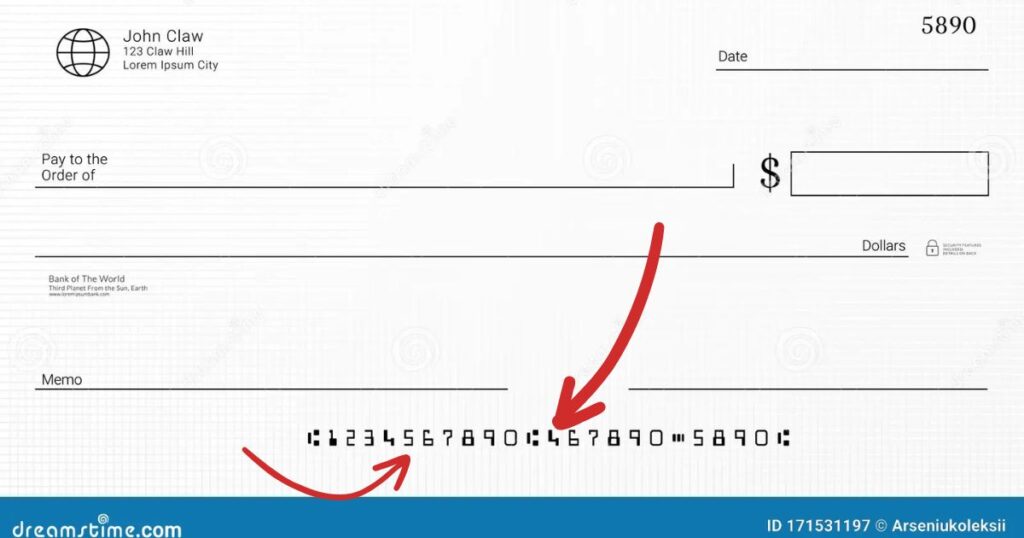
ABA transit numbers, also referred to as routing transit numbers or RTNs, are nine-digit codes assigned to financial institutions by the American Bankers Association (ABA). These numbers are structured as follows:
- The first four digits represent the Federal Reserve Routing Symbol, identifying the Federal Reserve District and region.
- The next four digits represent the financial institution’s unique identification number within that region.
- The final digit is a mathematical check digit used for validating the entire number.
For example, in the ABA transit number 123456789, the first four digits 1234 identify the Federal Reserve District and region, the next four digits 5678 represent the specific financial institution, and the final digit 9 is the check digit.
ABA transit numbers are primarily used for identifying financial institutions participating in the Fedwire Funds Service and other electronic funds transfer systems facilitated by the Federal Reserve Banks.
What is the Difference Between Routing Numbers and ABA Transit Numbers?
While routing numbers and ABA transit numbers share similarities, there is a key distinction in their usage:
- Routing numbers are used for all domestic transactions within the United States, including electronic transfers, direct deposits, and domestic wire transfers. They can also be used for international wire transfers originating or terminating in the U.S.
- ABA transit numbers are a specific type of routing number used primarily for Fedwire fund transfers and other services facilitated by the Federal Reserve Banks. They are not used for international wire transfers outside the Fedwire system.
In essence, all ABA transit numbers are routing numbers, but not all routing numbers are ABA transit numbers. Routing numbers have a broader scope of use, encompassing both domestic and international transactions, while ABA transit numbers are specific to domestic Fedwire transfers and related services.
Routing Numbers vs ABA Transit Numbers: Key Differences and Uses
To summarize the key differences and uses of routing numbers and ABA transit numbers:
Here’s the feature comparison table for Routing Numbers and ABA Transit Numbers:
| Feature | Routing Number | ABA Transit Number |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identifies financial institutions for domestic and international transactions | Identifies financial institutions for Fedwire transfers and Federal Reserve services |
| Structure | 9 digits, same format as ABA transit numbers | 9 digits, with specific digit assignments |
| Usage | Domestic transactions (ACH, direct deposit, wire transfers), international wire transfers | Fedwire fund transfers, Federal Reserve services |
| Issuing Authority | American Bankers Association (ABA) | American Bankers Association (ABA) |
It’s important to note that while routing numbers and ABA transit numbers serve distinct purposes, many financial institutions use the same nine-digit code for both. This means that for most domestic transactions, you can use the routing number provided by your bank as the ABA transit number, and vice versa.
However, for international wire transfers originating or terminating outside the United States, a separate routing number specifically for international transactions may be required. It’s always best to confirm the appropriate codes with your financial institution to ensure accurate and successful fund transfers.
Read More Also: Brook Taube Medley: The Visionary Co-CEO Transforming Financial Management
How to Find Your Routing and Transit Numbers?
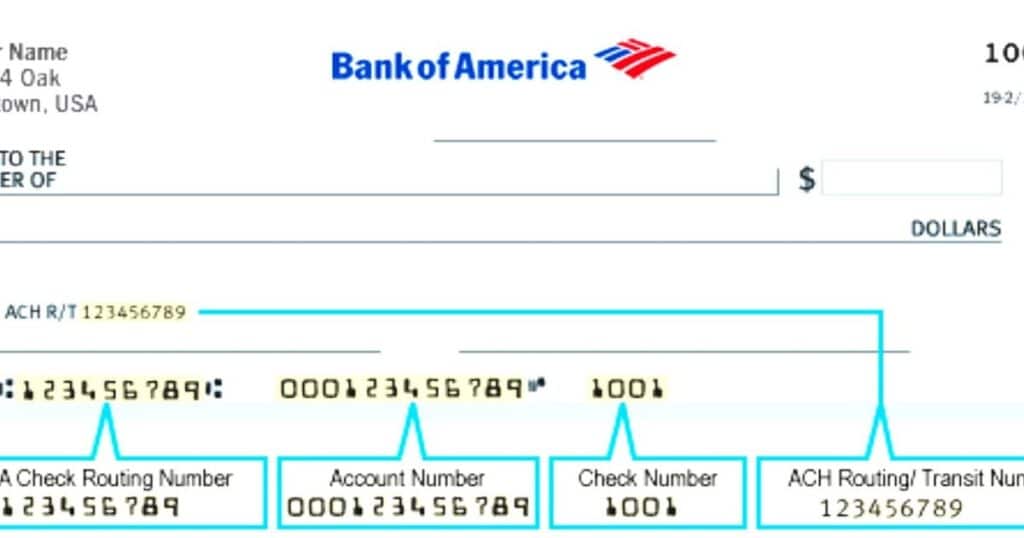
Locating your routing and transit numbers is relatively straightforward. Here are some common sources:
- Personal Checks: The routing number (and often the ABA transit number) is typically printed at the bottom left corner of personal checks, preceding the account number.
- Bank Statements: Both routing and transit numbers are usually listed on monthly bank statements.
- Online Banking: Most banks provide routing and transit numbers through their online banking portals or websites.
- Bank Branch: Visit your local bank branch, and a representative can provide you with the necessary codes.
It’s important to ensure you have the most up-to-date numbers, as routing and transit numbers can occasionally change due to bank mergers, acquisitions, or other administrative changes.
Why are Routing and Transit Numbers Important?
Routing and transit numbers play a critical role in facilitating accurate and secure financial transactions. Some key reasons why they are essential:
- Identifying Financial Institutions: These numbers serve as unique identifiers, ensuring funds are correctly routed to the intended bank or credit union.
- Enabling Electronic Transactions: Routing and transit numbers are required for setting up direct deposits, electronic bill payments, and transferring funds between accounts.
- Facilitating International Transfers: For international wire transfers, routing numbers ensure funds are properly directed across borders and banking systems.
- Preventing Errors and Fraud: Incorrect or outdated routing/transit numbers can lead to returned payments, delays, and potential financial losses. Proper use of these codes helps maintain the integrity of the financial system.
According to the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA), routing number errors account for a significant portion of returned or rejected ACH payments each year, costing businesses and consumers time and money.
How to Use Routing and Transit Numbers?
Routing and transit numbers are commonly required in various financial scenarios, such as:
- Setting up Direct Deposit: Provide your routing and account numbers to your employer for convenient direct deposit of your paycheck.
- Scheduling Electronic Payments: Enter routing and account numbers when scheduling online bill payments or automatic recurring payments.
- Transferring Funds Between Accounts: Use routing numbers to facilitate transfers between accounts at different financial institutions.
- Initiating Wire Transfers: For domestic wire transfers, provide your bank’s routing number, and for international wires, use the appropriate code for cross-border transactions.
When entering routing and transit numbers, it’s essential to double-check the digits for accuracy. Even a single incorrect digit can result in payment delays or funds being misdirected.
Many financial institutions and online payment platforms provide clear instructions and designated fields for entering routing and account numbers correctly.
Frequently Asked Questions about Routing and Transit Numbers
Are routing numbers and ABA transit numbers the same thing?
While they share similarities, routing numbers have a broader scope, encompassing both domestic and international transactions, while ABA transit numbersUnravel the mystery of routing numbers and ABA transit numbers. This comprehensive guide explains their differences, purposes, and importance for secure financial transactions. are primarily used for Fedwire transfers and Federal Reserve services within the United States.
Can I use my ABA transit number for international wire transfers?
No, for international wire transfers originating or terminating outside the U.S., a separate routing number specifically for international transactions may be required. Confirm with your bank for the appropriate codes.
Do routing and transit numbers ever change?
Yes, routing and transit numbers can occasionally change due to bank mergers, acquisitions, or administrative updates. Always verify you have the most current codes with your financial institution.
What happens if I use the wrong routing or transit number?
Using incorrect routing or transit numbers can lead to returned payments, delays, and potential fees or financial losses. Double-checking these codes is crucial for accurate fund transfers.
Where can I find my routing and transit numbers?
Common sources include personal checks, bank statements, online banking portals, and your local bank branch. Contact your financial institution if you cannot locate these codes.
Conclusion
Routing numbers and ABA transit numbers may seem like a small detail, but they play a vital role in the complex world of financial transactions. Understanding their differences and proper usage ensures funds are accurately and securely routed between accounts and institutions.
Remember, routing numbers are used for all domestic transactions within the U.S., as well as international wire transfers, while ABA transit numbers are specific to Fedwire transfers and Federal Reserve services. Many financial institutions use the same nine-digit code for both purposes, but it’s always wise to confirm the appropriate codes with your bank,

Howdy, editor at FinanceEon.com, brings over a decade of financial journalism experience. He ensures accuracy and insightful analysis, guiding a team on market trends and investment strategies.







